Nitrogen & Phosphorous are two major nutrients for plant growth which are provided through Chemical Fertilizers or Organic Manure. Certain soil microorganisms have an ability to fix part of elementary form of atmospheric nitrogen to the available form for the plants and/or solubilize part of the bound phosphates of the soil and thereby make them available to the plant which increases fertility of the soil and yield. These characteristics make them useful as Bio-fertilizers.
Thus, the Bio-fertilizers are the ‘Live Fertilizers’ of biological origin.
Advantages of Biofertilizers in general :
- Harmless and Eco-friendly low cost agro-input.
- Higher Shelf-life.
- Higher bacterial count.
- Add nutrients to the soil / make them available to the crop & secret certain growth promoting substances.
- Help the proliferation and survival of beneficial microorganisms in soil.
- Under certain conditions it exhibit anti-fungal activity and thereby protects the plant from pathogenic fungus.
- Increase soil fertility and crop production.
- Varied application methods including Drip Irrigation.
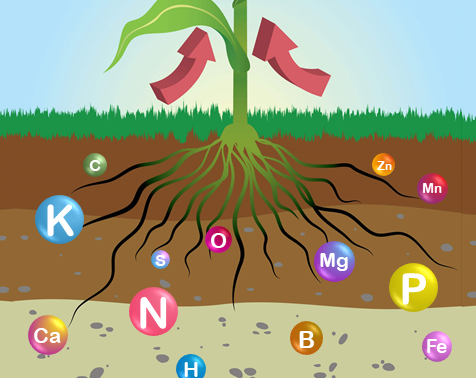
Role of nutrients on plant :
Nitrogen (N)
- Nitrogen encourages vegetative growth and imparts dark green colour to plants.
- Regulates the utilization of P and K and other constituent.
Phosphorus (P)
- P stimulates root development and growth in seedling stage and thereby it helps to establish the seedling quickly.
- It hastens leaf development and encourages grater growth of shoots and roots.
- It stimulates the flowering, fruit setting and seed formation and development of roots, particularly of root crops.
- It includes nodule formation of leguminous crop and rhizobial activity.
Potash (K)
- It is important element for the development of chlorophyll.
- It is essential for photosynthesis and translocation of sugar.
- Improves the health and vigour of the plant
- It strengthens the straw of cereals and reduces lodging.
- It improves the quality of grains.
- It increases the crop resistance against certain diseases and counteracts the damaging effect of excess nitrogen.
Zinc (Zn)
- Takes part in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
- It is involved in the biosynthesis of plant growth hormone (IAA) and in the reproduction of certain plants.
- It has a positive role in the photosynthesis and metabolism.
- It is required for seed role seed production.
